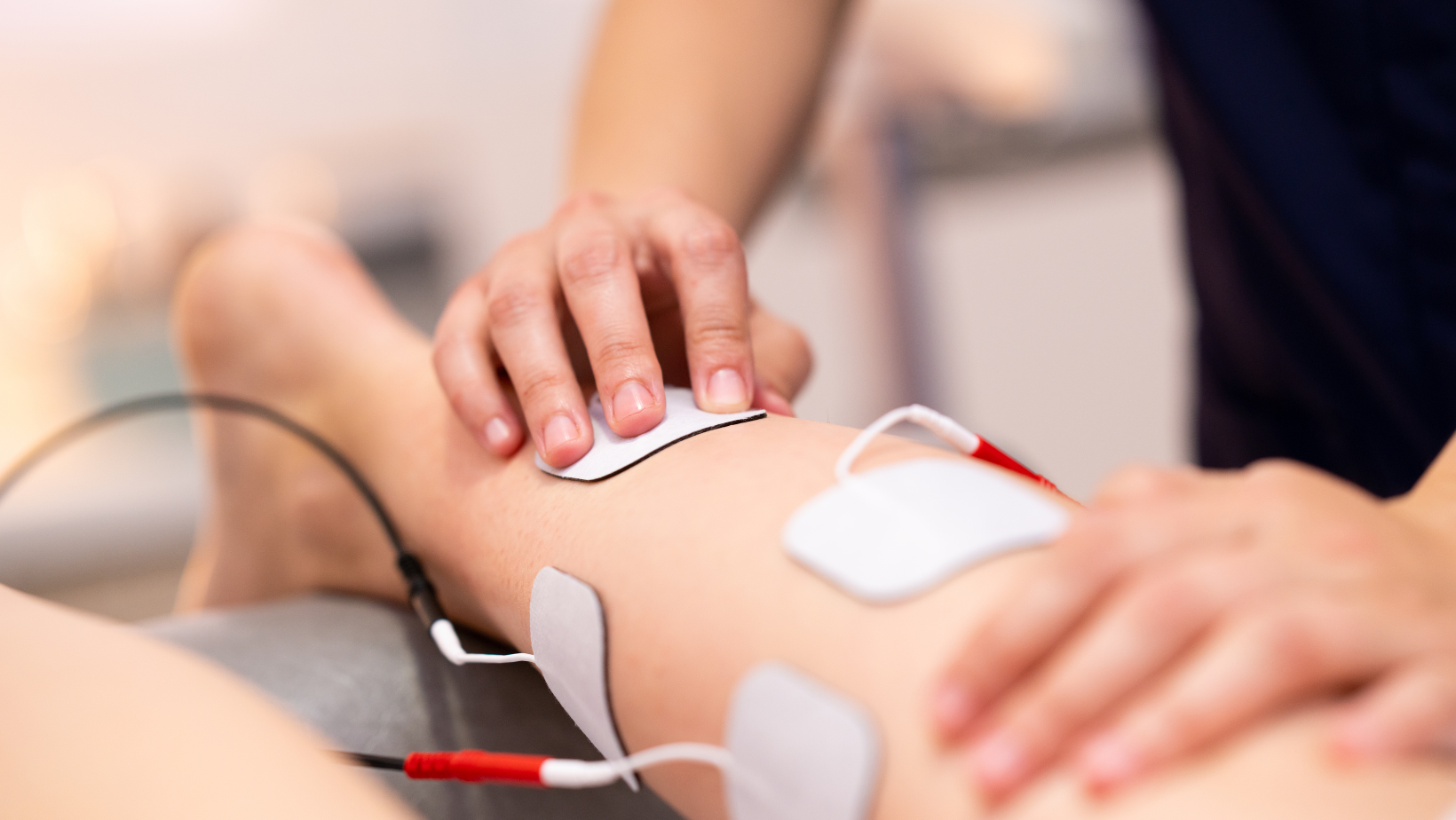
What is an Electrical Stimulation Unit (stim)? It is a machine commonly used by Physical Therapists as part of a patient plan of care. It serves as a safe, non-invasive way to help manage pain and improve muscle function by delivering mild electrical currents through the skin.
How Stim Units Work
Stim units work by applying adhesive electrodes to the skin near the targeted muscles or nerves. The machine then sends controlled electrical pulses into the body to produce specific therapeutic effects.
There are two ways stim units can be used:
Nerve Stimulation (Pain Relief): The electrical pulses target sensory nerves to block or interfere with pain signals traveling to the brain, which changes the perception of pain. It also encourages the body to produce natural pain-relieving chemicals called endorphins.
Muscle Stimulation (Rehabilitation): Stronger currents target motor nerves, causing the muscles to contract and relax rhythmically. This mimics natural muscle movement, helping to maintain or increase muscle strength, prevent atrophy (muscle shrinking), improve blood flow, and reduce muscle spasms.
Types of Stim Units in Physical Therapy
Physical Therapists use various types of stim, depending on the patient’s condition and goals:
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Primarily used for pain relief (acute and chronic) by targeting sensory nerves.
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES): Focuses on muscle rehabilitation by causing muscle contractions to improve strength, function, and motor control.
Interferential Current (IFC): Uses higher-frequency currents that penetrate deeper into tissues for more profound pain relief and to reduce deep inflammation and swelling.
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Used for individuals with nerve damage or neurological conditions (like stroke or spinal cord injury) to help regain lost motor function and perform functional tasks such as walking or grasping objects.
Benefits of Stim Therapy
When combined with other active physical therapy treatments, stim can help to:
- Reduce or eliminate pain and muscle spasms.
- Prevent muscle atrophy and maintain muscle mass.
- Improve muscle strength and control.
- Increase blood circulation to promote faster healing.
- Decrease swelling and inflammation.
- Enhance range of motion.
- Help re-educate muscles to contract properly after injury or stroke.
Stim is generally used as part of a comprehensive rehabilitation plan in physical therapy. Your Physical Therapist will determine the appropriate type and intensity of stim for your specific condition and treatment.